A breed of huge wild cattle could effectively be reintroduced to Scotland four centuries after becoming extinct.
Trees for Life aims to introduce a herd of up to 15 tauros from the Netherlands to its 4,000-hectare Dundreggan estate near Loch Ness in 2026.
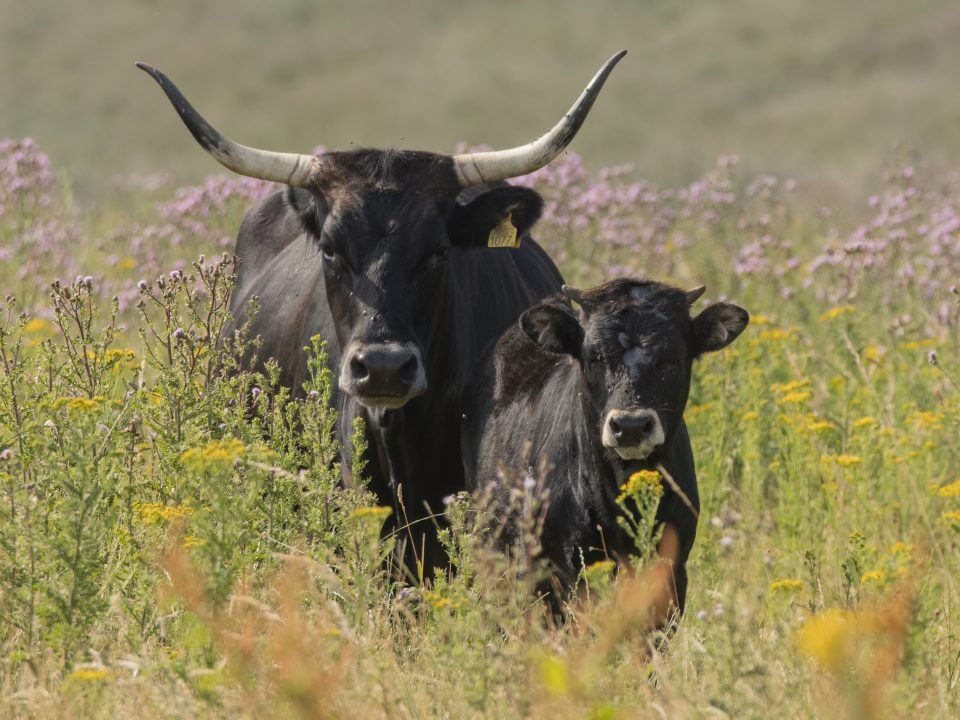
The muscular, long-horned tauros have been bred to be as similar as possible to the ancient aurochs – a mega-herbivore that for millennia played a vital role in shaping landscapes and boosting biodiversity across Europe, including Scotland.
The aurochs are known as the wild ancestor of all domestic cattle.
Steve Micklewright, chief executive of Trees for Life, said: “Introducing the aurochs-like tauros to the Highlands four centuries after their wild ancestors were driven to extinction will refill a vital but empty ecological niche – allowing us to study how these remarkable wild cattle can be a powerful ally for tackling the nature and climate emergencies.”
“Our Tauros Project is about looking forwards while learning from the past as we restore nature-rich landscapes that support wildlife and people, and are resilient to future environmental challenges.
“We also want to give people the chance to experience in a safe way the awe and wonder of getting close to an animal that feels really wild.”
Aurochs once roamed much of Europe as a keystone species, ensuring a rich mosaic of habitats including grasslands, forest, and wetlands. The animals are depicted in petroglyphs of the Côa Valley, dating back 30,000 years.
One of Europe’s largest land mammals – and the heaviest after the woolly mammoth and woolly rhinoceros – aurochs disappeared from Britain around 1300 BC.
They later became globally extinct through habitat loss and hunting, when the last aurochs died in Poland in 1627. But aurochs DNA has survived in a number of ancient original cattle breeds.
Uniquely, tauros have been ‘back-bred’ to genetically replicate, resemble and behave like the aurochs as closely as possible.
Scientists in the Netherlands have sought to bring aurochs back to life since the early 2000s, by interbreeding ancient cattle breeds that are genetically and physically closest to the aurochs. This has been aided by the first sequencing of the aurochs’ complete genome, in 2011.
While classified as domestic cattle, tauros have no equivalent among other breeds. Bulls can reach up to 180cm and cows 150cm at the shoulder, similar in size to aurochs. They can live in a wide range of environmental conditions, with minimal human intervention.
Research in Europe shows these modern-day successors to the aurochs can help create exceptionally rich habitats for wildlife through their size and behaviour – being bigger and more active than other cattle, and interacting with their environment more dramatically.
Herds of tauros move across landscapes in social groups, naturally grazing some areas intensively while leaving others untouched. This creates a mosaic of habitats that benefit a wide range of plants and animals, boost species diversity, and soak up carbon dioxide.
There are already several hundred tauros in mainland Europe, in The Netherlands, Czechia, Croatia, Spain and Portugal.
Follow STV News on WhatsApp
Scan the QR code on your mobile device for all the latest news from around the country

 Grazelands Rewilding
Grazelands Rewilding